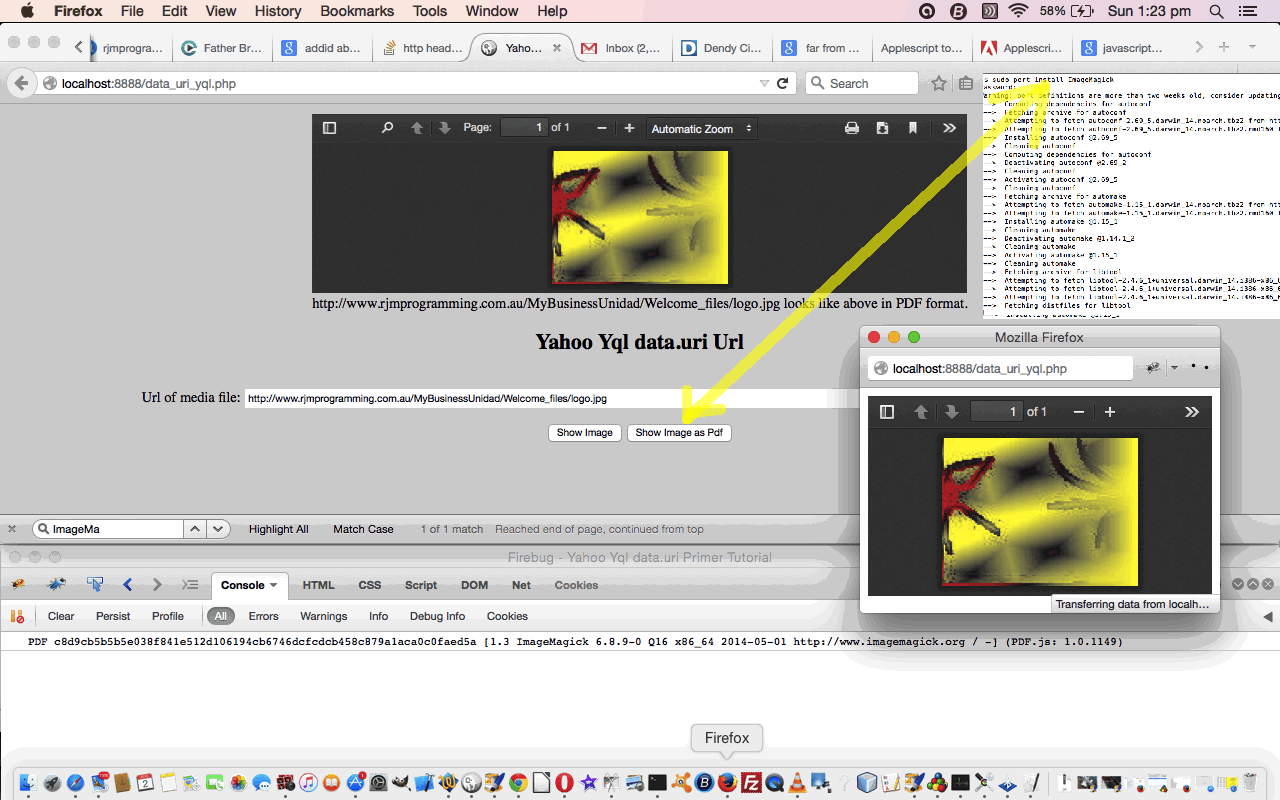
Today, we follow up on yesterday’s Yahoo YQL Web Service JSON data.uri Tutorial as shown below, by adding a display in PDF of the image data, as an extra piece of functionality.
We use the incredibly useful PHP ImageMagick class functionality to do the conversion to PDF from the image formats, and only perform the conversion if the data uri is possible to use via the use of the Yahoo YQL Web Service data.uri methods.
As this involves storing files on a server, so there is the necessity of using a server-side language like PHP. We restrict PDF display to image files on the //www.rjmprogramming.com.au domain, as these are files I’m happy for you to try, so, if you have trouble finding these, you can examine //www.rjmprogramming.com.au domain webpages and use …
- View->Page Source web browser options … or a …
- Web Inspector (like Firefox’s Firebug) … or …
- Right Click an image and get image information
… but, as for yesterday, bear in mind that there is a 25600 byte limit to the Yahoo YQL data.uri Web Service conversions.
It is not only this type of conversion that the PHP ImageMagick class functionality can help with, and we strongly encourage you to examine it more as a wonderful tool for graphics and media work. We installed it onto our local MAMP server via the MacPorts command (in the Mac application Terminal) …
sudo port install ImageMagick
… as you can see over to the top right of today’s tutorial picture.
We’ll leave you today with our PHP code you could call data_uri_yql.php which changed from yesterday’s code in this way.
Previous relevant Yahoo YQL Web Service JSON data.uri Tutorial is shown below.
Here is a tutorial that might be re-introducing you to the Yahoo Web Services called YQL, building on previous ones here at this blog. The name is the way it is because it simplified the API aspects of its functionality for the developer to concentrate on SQL, and I’m really supportive of this concept. You don’t have to output in JSON, as other data forms like XML are acceptable. Let’s see what Wikipedia says about YQL below.
Yahoo! Query Language (YQL) is an SQL-like query language created by Yahoo! as part of their Developer Network. YQL is designed to retrieve and manipulate data from APIs through a single Web interface, thus allowing mashups that enable developers to create their own applications.[1]
Initially launched in October 2008 with access to Yahoo APIs,[2] February 2009 saw the addition of open data tables from third parties such as Google Reader, the Guardian, and The New York Times.[3] Some of these APIs still require an API key to access them. On April 29th of 2009, Yahoo introduced the capability to execute the tables of data built through YQL using JavaScript run on the company’s servers for free.[3]
So this tutorial uses a YQL web service into the data emanating from its links to the data.uri web service database with Yahoo YQL website … thanks.
We’ve talked in passing about the data.uri concept before. In the case of an HTML img tag’s definition you can specify the src= value in three different ways …
- as an address via an http: or https: protocol URL such as //www.rjmprogramming.com.au/MyBusinessUnidad/Welcome_files/logo.jpg (our default)
- as an address via a local file: protocol URL such as file:///Library/pgAgent/Desktop/dynamic_javascript.jpg accessing a local image on the local computer being used (like you can make happen when you access your web browser’s File->Open File… functionality)
- as a data uri value which is a way to fully define the image data there and then, using base64 data
What this data.uri Yahoo Yql web service is providing, is a way to create a data uri from an http: or https: URL definition of a media file (image in our thinking above) … but, please note there is a 25600 byte limit to the size of the media file.
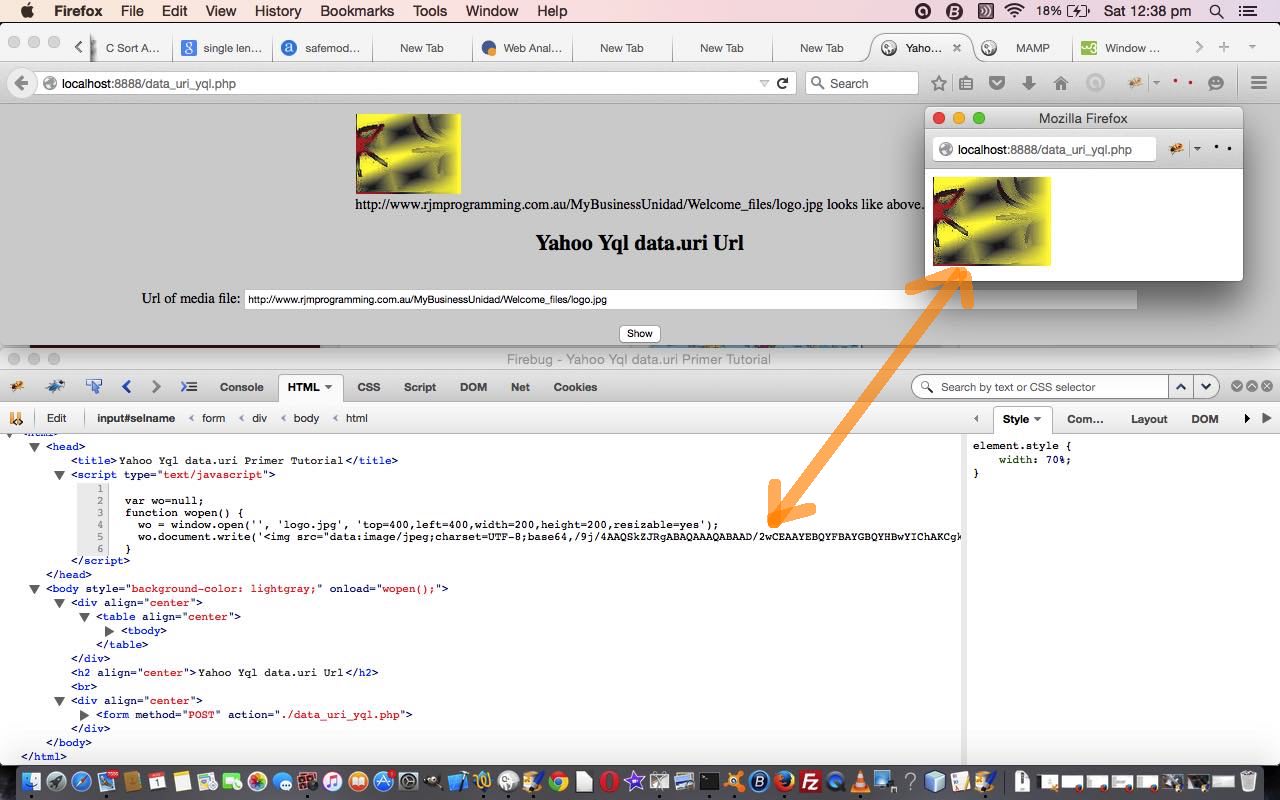
In our application today we show you an HTML img tag of the data on the parent page (the Firefox browser Firebug add on is showing you the resultant data uri) with a Javascript code scenario …
var thedatauri = 'data:image/jpeg;charset=UTF-8;base64,<!-- base64 data -->';
var wo=window.open('', 'imagename.jpg', 'top=400,left=400,width=200,height=200,resizable=yes');
wo.document.write('<img src="' + thedatauri + '" />');
… arranged by today’s PHP code you could call data_uri_yql.php or try a live run. In that way the HTML img data of the resultant popup window has no reference to any particular address on the web and would be useful for document fidelity purposes perhaps, as we’ve discussed previously on the blog here, because there is no trail back regarding its metadata.
Good links for information regarding this tutorial (thanks) are:
- YQL Two Minute Tutorial from Yahoo
- Yahoo! Query Language from Wikipedia, as per quote above
- YQL Home Page from Yahoo
- YQL data.uri help from Yahoo
- YQL JSON Parsing Help from YQL forum
Another tool you should have in your armoury for jobs like this is the online JSON validator here. A generic JSON approach to issues could be:
- Type the URL you were given into a web browser address bar and have a look at it
- Type the URL you were given into //jsonlint.com/ and have it validated
- Understand in your own mind what would be different about 1. to make it suitable
- Incorporate findings of 3. into massaging of data between file_get_contents and json_decode
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.
If this was interesting you may be interested in this too.